Net Tribe Carbon System Overview
Quick stat: The global voluntary carbon market was worth USD 2B in 2023 and could grow to USD 250B by 2030, yet Africa contributes <3% of credits despite huge renewable and e-mobility potential. Africa has 48M motorcycles, a sector projected to reach USD 5.07B by 2030, with petrol bikes contributing up to 40% of urban pollution in East Africa. Electric motorcycles are 70% cheaper to operate, while riders in Kenya currently spend KES 400–600 daily on fuel (~40% income). Battery swapping cuts downtime from 6 hours to 2 minutes, and solar-powered charging reduces lifetime emissions by 90%. Connecting just 1M motorcycles could generate 4–6 MtCO₂ credits annually (~USD 400–600M value), while scaling across Africa could avoid 5.7 GtCO₂ over 25 years.
Executive summary
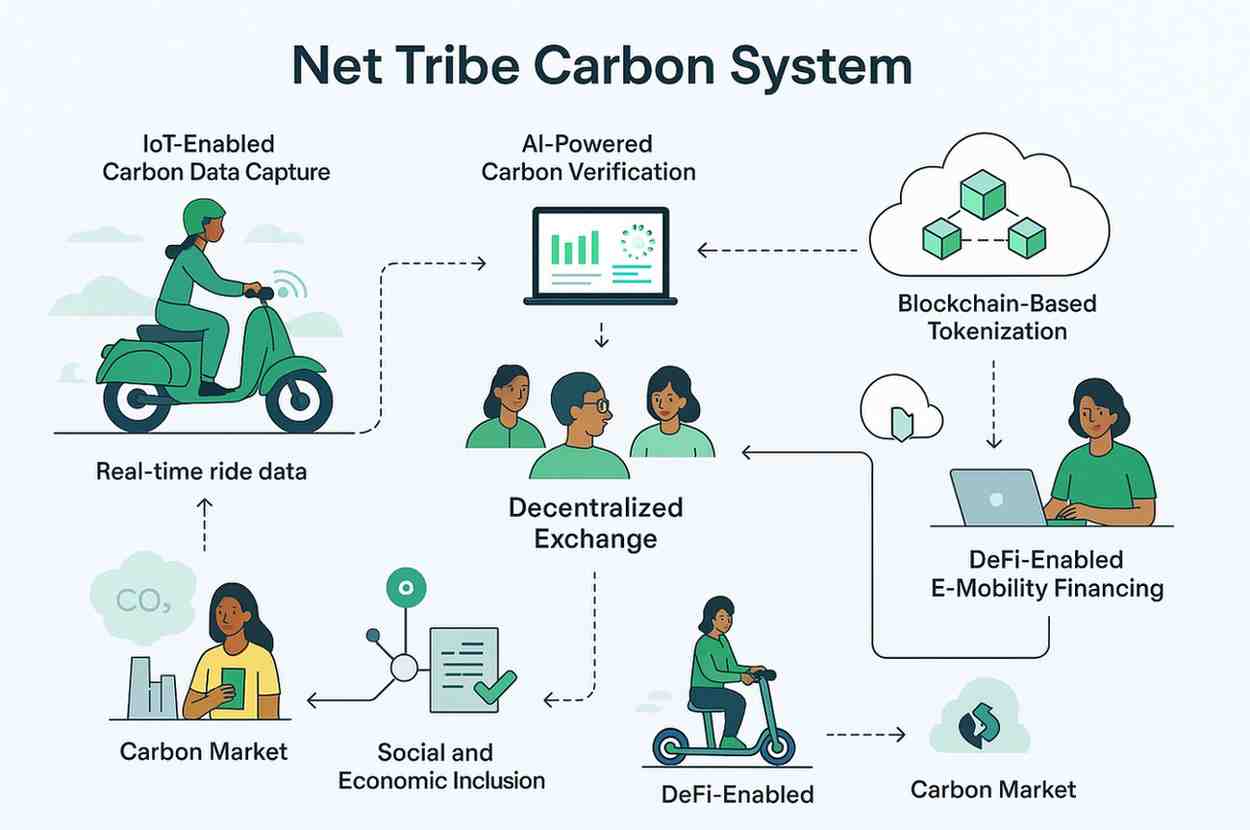
Net Tribe Carbon is a technology-first platform that closes the MRV and finance gaps blocking mass electrification of two-wheel mobility in Africa. By combining IoT, AI, blockchain tokenization and DeFi financing, the system measures avoided CO₂ in real time, mints high-integrity carbon tokens, and unlocks affordable finance for riders and fleets.
Problem statement — why Net Tribe Carbon exists
The transport sector is the fastest-growing source of energy-related CO₂ emissions, responsible for roughly 23% of global energy CO₂ (IEA, 2024). In many African and Asian cities, two- and three-wheelers dominate urban mobility and are a substantial contributor to local air pollution and greenhouse gases.
In Kenya, there are approximately 2.7 million registered motorcycles (NTSA, 2023), roughly 95% of which run on fossil fuels. Using a locally calibrated baseline of 0.12 kg CO₂/km, the national motorcycle fleet emits an order of tens of millions of tonnes of CO₂ annually — a large and rapidly growing emissions source.
- Financing gap: electric motorcycles cost 30–50% more than ICE equivalents; many riders lack credit history and affordable lending products.
- MRV & verification bottlenecks: conventional carbon methodologies are costly ($100k+ audits), slow, and poorly suited to micro-scale, distributed emission reductions.
- Market access: voluntary carbon markets value is growing (from ~$2B in 2023 toward projections in the tens of billions by 2030), but African projects and micro initiatives remain under-represented.
The combined effect: frontline riders and small e-mobility fleets cannot monetize their climate impact, limiting their ability to access finance, expand operations, and recruit riders (especially women). Carbon buyers and investors, in turn, lack trustworthy, traceable, African-sourced credits with granular provenance.
Deep-dive: the systemic barriers
- Technological integration challenge: streaming, securing and validating millions of micro-trips in real time while ensuring tamper resistance.
- Methodological rigor: creating a transparent MRV methodology robust enough for registries and buyers, while remaining cost-efficient for small operators.
- Scalable financing: transforming sporadic carbon value into reliable collateral and financial instruments that lenders accept.
Without a solution that addresses these three failure points together, the e-mobility transition stalls: riders can’t buy EVs, fleets can’t scale, and cities stay locked into polluting transport.
Net Tribe Carbon — solution overview
Net Tribe Carbon is an end-to-end platform that captures ride-level telemetry, verifies avoided emissions with AI, mints tokenized carbon credits on blockchain, and channels finance to riders via DeFi and partner lenders. The platform is designed to be low-cost, auditable, and inclusive.
Core component
- IoT Carbon Capture: low-power GPS + energy meters record distance, kWh used, and ride behavior. Edge buffering enables offline operation.
- AI Verification Engine: machine-learning models compute avoided CO₂ (baseline ICE gCO₂/km minus EV energy × grid factor), detect anomalies, and produce verification proofs.
- Blockchain Tokenization: verified CO₂ is minted as asset-backed tokens (ERC-1155 style) with on-chain metadata and IPFS-stored proofs.
- DeFi Financing Layer: token streams serve as collateral for microloans and lease-to-own programs; repayments automated via smart contracts.
- DEX & Marketplace: instant trading, staking and retirement of tokens for buyers, investors and corporates seeking high-integrity offsets.
- EoT Platform: Asset backed tokens represent physical electric motorcycles. Investors purchase these tokens and lease them digitally to riders, who use the motorcycles for daily income. Smart contracts automate revenue-sharing, allowing investors to earn either a fixed daily lease fee or a 10% share of rider earnings, creating a sustainable income stream while expanding e-mobility access.
Data, MRV methodology & fraud controls
Primary telemetry collected: GPS route & geofencing, km per trip, battery voltage/current (kWh), timestamps, speed profiles, swap logs, device health and tamper flags.
AI models (anomaly detectors, RL agents for pattern recognition) flag suspicious telemetry. Cross-validation uses charging station logs, identity checks (mobile IDs), and hashed telemetry stored on the ledger for an audit trail. Periodic independent audits and registry-ready export formats keep the system compatible with voluntary and compliance registries.
Tokenization, market mechanics & rider finance
Verified CO₂ is tokenized as tradable units. Units can be fractionalized and aggregated into pools for institutional buyers. Token economy features:
- 1 token = 1 tCO₂e (or fractionalized as 0.01 t), minted with hashes linking back to ride IDs and verification proofs.
- Collateralized lending: riders stake future token streams for microloans or lease payments; repayments automated from token revenues.
- Revenue split: issuance fees, marketplace fees, SaaS/API revenues, and licensing the verification engine.
This creates a circular finance model: tokens underwrite access to EVs → EVs create verified emissions reductions → reductions mint tokens → tokens finance more EVs.
Pilots, feasibility & early impact
A pilot deployment generated measurable early wins:
- 576 tCO₂ avoided (pilot period).
- 18,000 trips logged from 120 connected e-motorcycles.
- Carbon asset value generated: $57,600 (at $100/tCO₂ reference price for illustration).
The architecture addresses low connectivity (edge compute + LoRa/GSM hybrid), device security (signed firmware & tamper flags), and data integrity (hashed telemetry & IPFS).
KPIs, targets & social goals
- Year 1 (pilot scale): 5,800 tCO₂e (scaling operations)
- Year 5 target: 64,800 tCO₂e with ~12,000 riders onboard
- Rider uplift metrics: income increase %, retention, jobs created
- Inclusion: 70% of riders prioritized for women and youth outreach
Operational KPIs include model accuracy, false positive rate for anomaly detection, tokens issued/retired, loans disbursed against tokens, and timely payouts to riders via mobile money.
Risks & mitigations
- Regulatory risk: design permissioned ledger options, adopt compliance-first approach and engage regulators early.
- Data fraud: multi-sensor validation, anomaly detection, hashed telemetry and periodic physical audits.
- Market volatility: price-floors, diversified buyers and blended revenue (grants + carbon sales + debt).
- Tech reliability: edge caching, opportunistic sync, SMS fallback for critical events in low-connectivity zones.
- Social resistance: community engagement programs, female mentors and partnerships with local women’s organizations.
Conclusion — why Net Tribe Carbon is scalable
Net Tribe Carbon combines ground-truth assets (fleets) with scalable IP (AI verification, tokenization APIs & SaaS) to create a replicable, high-margin product after demonstration. The physical fleet proves integrity and builds buyer confidence; the software and methodology are the scalable asset. By aligning climate action with financial inclusion, this model unlocks both social impact and investable returns.
Short references (data sources used in this paper):
- International Energy Agency (IEA) transport emissions data (2024)
- National Transport and Safety Authority (NTSA), Kenya motorcycle registrations (2023)
- African Development Bank (AfDB) financing gap assessments
- Voluntary carbon market reports (McKinsey / market analyses)
